
Understanding Childhood Vaccines
A Guide for Parents and Guardians
Ensuring the health and safety of your child is a top priority for every parent. Vaccination plays a vital role in protecting children from potentially harmful and life-threatening diseases. In this essay, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the purpose of each vaccine recommended for your child and why they are administered at specific ages.
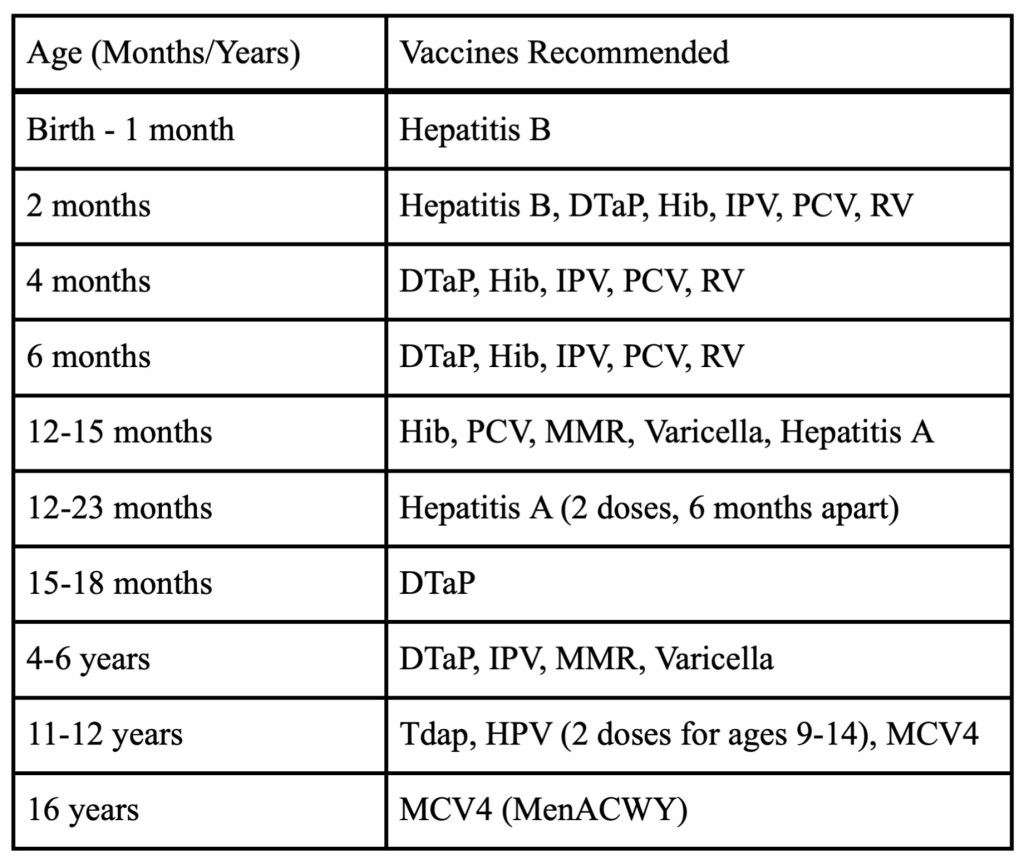
1. Hepatitis B: Hepatitis B vaccine protects against hepatitis B virus, which can cause liver inflammation and lead to serious liver damage or even liver cancer. Given shortly after birth to provide early protection against hepatitis B infection, which can be transmitted from an infected mother during childbirth.
2. DTaP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis): DTaP vaccine protects against three diseases: diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis (whooping cough). Administered in a series of doses starting at 2 months of age to provide immunity against these diseases before children are at risk of exposure.
3. Hib (Haemophilus influenzae type b): Hib vaccine protects against Haemophilus influenzae type b bacteria, which can cause severe infections such as meningitis and pneumonia. Given in a series of doses starting at 2 months of age to prevent Hib-related illnesses during infancy and childhood.
4. IPV (Inactivated Poliovirus): IPV vaccine protects against poliovirus, which can cause polio, a highly infectious disease that can lead to paralysis or even death. Administered in a series of doses starting at 2 months of age to provide immunity against poliovirus.
5. PCV (Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine): PCV vaccine protects against pneumococcal bacteria, which can cause serious infections such as pneumonia, meningitis, and bloodstream infections. Given in a series of doses starting at 2 months of age to prevent pneumococcal-related illnesses during infancy and childhood.
6. RV (Rotavirus): RV vaccine protects against rotavirus, a common cause of severe diarrhea and dehydration in infants and young children. Administered in a series of doses starting at 2 months of age to provide early protection against rotavirus infection.
7. MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella): MMR vaccine protects against measles, mumps, and rubella (German measles), three highly contagious viral infections. Given at 12-15 months of age to provide immunity against these diseases before children enter school and are at higher risk of exposure.
8. Varicella (Chickenpox): Varicella vaccine protects against varicella-zoster virus, which causes chickenpox, a highly contagious viral infection characterized by a rash and fever. Given at 12-15 months of age to provide immunity against chickenpox.
9. Hepatitis A: Hepatitis A vaccine protects against hepatitis A virus, which can cause liver inflammation and lead to illness ranging from mild to severe. Given in two doses, with the first dose administered at 12-23 months of age and the second dose administered 6 months later, to provide immunity against hepatitis A.
10. Tdap (Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis): Tdap vaccine provides booster doses of protection against tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (whooping cough) for adolescents and adults. Given at 11-12 years of age to reinforce immunity against these diseases before adolescence.
11. HPV (Human Papillomavirus): HPV vaccine protects against human papillomavirus, which can cause various cancers including cervical cancer, as well as genital warts. Given in a series of doses starting at 11-12 years of age to provide protection against HPV before potential exposure.
12. MCV4 (Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccine): MCV4 vaccine protects against meningococcal bacteria, which can cause meningitis and bloodstream infections. Given at 11-12 years of age with a booster dose at 16 years of age to provide immunity against meningococcal disease during adolescence and early adulthood.
Vaccines are a cornerstone of preventive healthcare for children, offering protection against a range of infectious diseases. By following the recommended vaccination schedule, you can ensure your child receives the necessary protection at the right time. If you have any questions or concerns about vaccines, do not hesitate to discuss them with your pediatrician. Together, we can work towards keeping your child healthy and safe.